Possible causes of pain in the right upper arm.
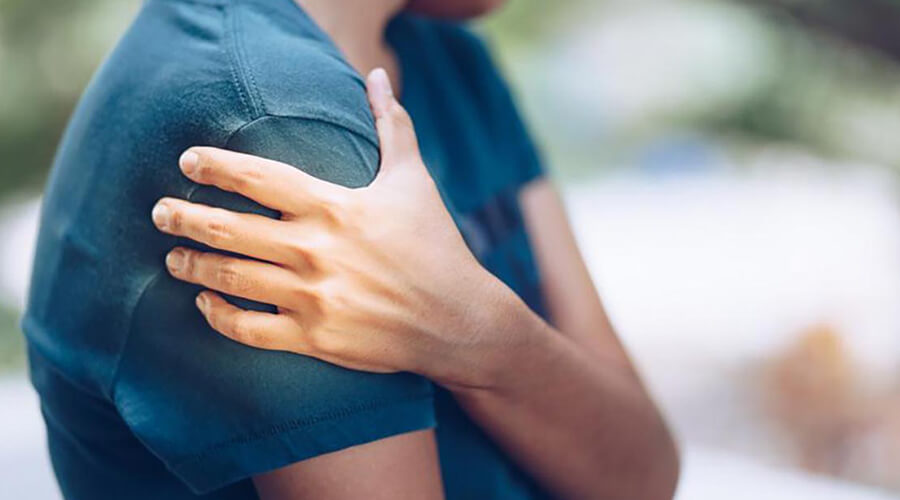

Right upper arm pain can result from conditions like muscle strain, rotator cuff injuries, nerve compression, or issues with the shoulder, heart, or spine.

Right upper arm pain can result from conditions like muscle strain, rotator cuff injuries, nerve compression, or issues with the shoulder, heart, or spine.
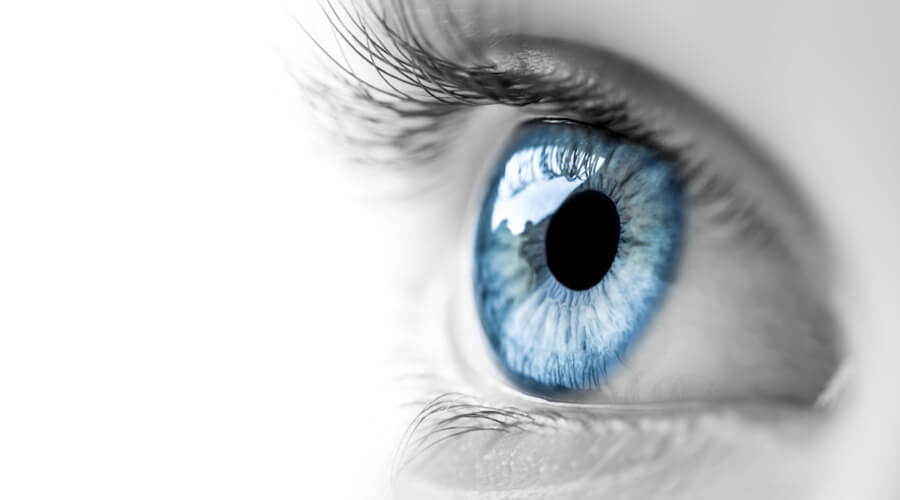

Home remedies for eye inflammation include using cold compresses, aloe vera, chamomile tea bags, and practicing proper eye hygiene to reduce irritation and swelling.
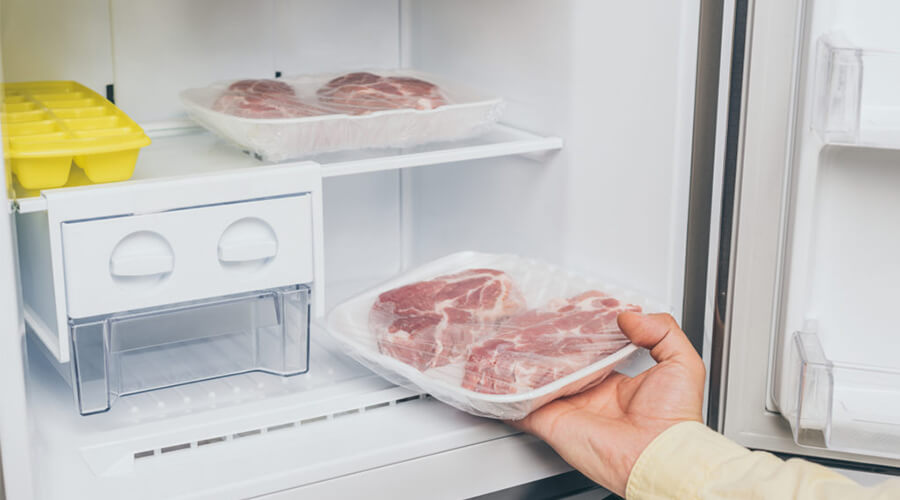

Meat can be stored in the refrigerator for 1-5 days depending on the type (poultry, beef, pork) and condition. Proper storage in airtight containers extends freshness.
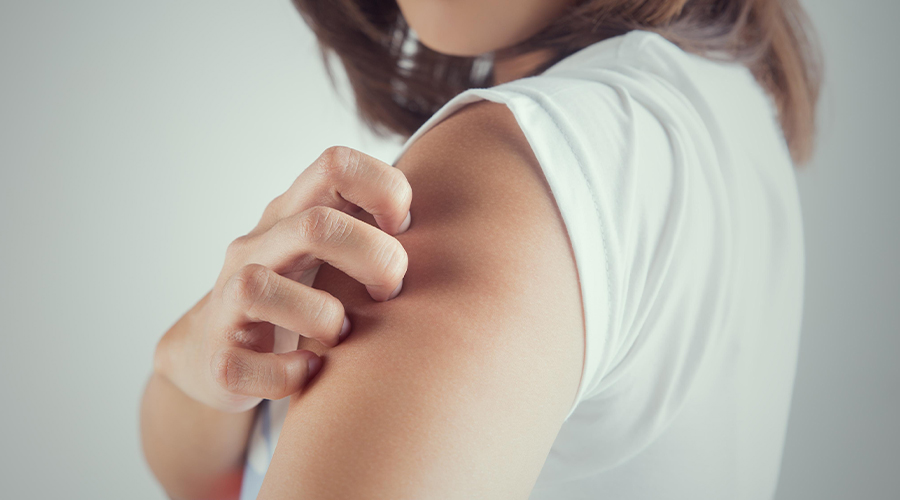

Itching can signal conditions like allergies, skin infections, eczema, liver disease, or diabetes. Identifying the cause is key to proper treatment and relief.
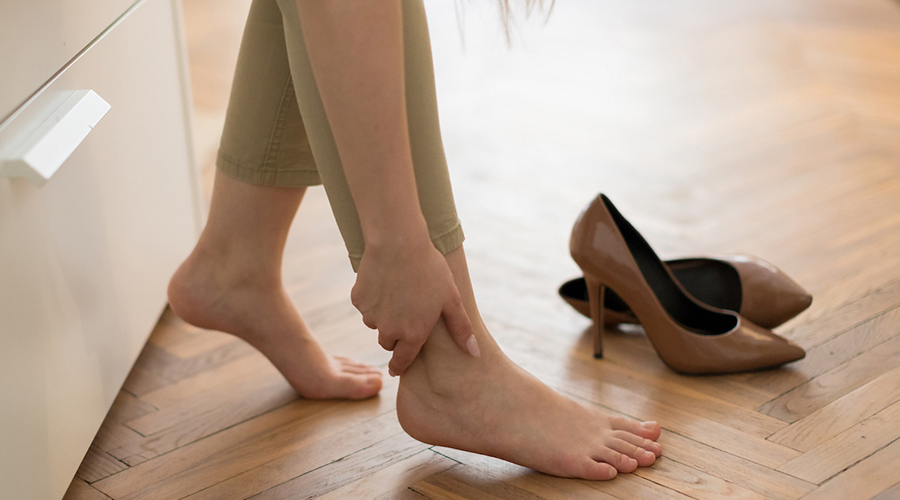

Swollen feet can be caused by conditions like poor circulation, injury, kidney disease, or heart problems. Identifying the cause is essential for proper treatment.
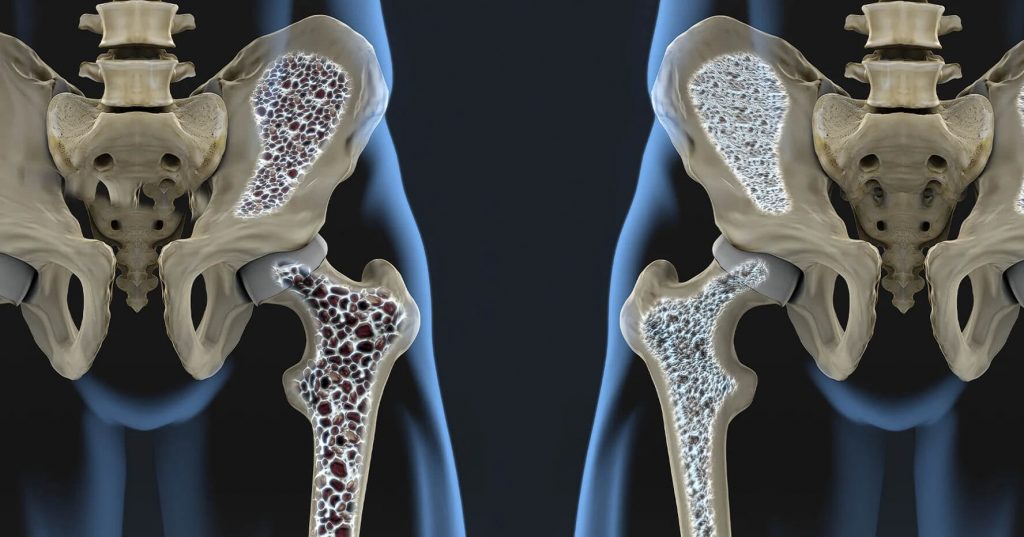
Common signs of calcium deficiency include brittle nails, muscle cramps, numbness, fatigue, poor bone health, and irregular heartbeats. Seek medical advice for diagnosis.
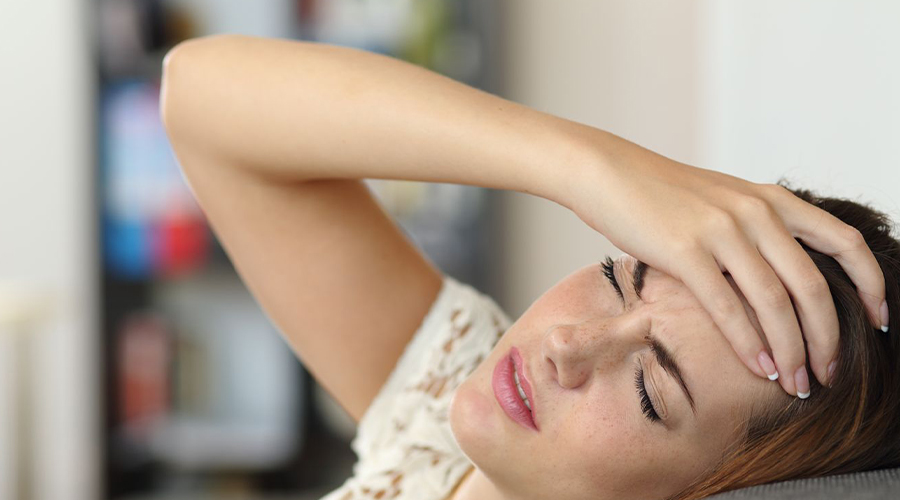

Iron deficiency symptoms include fatigue, pale skin, shortness of breath, dizziness, brittle nails, and headaches. If these occur, consider getting a blood test.
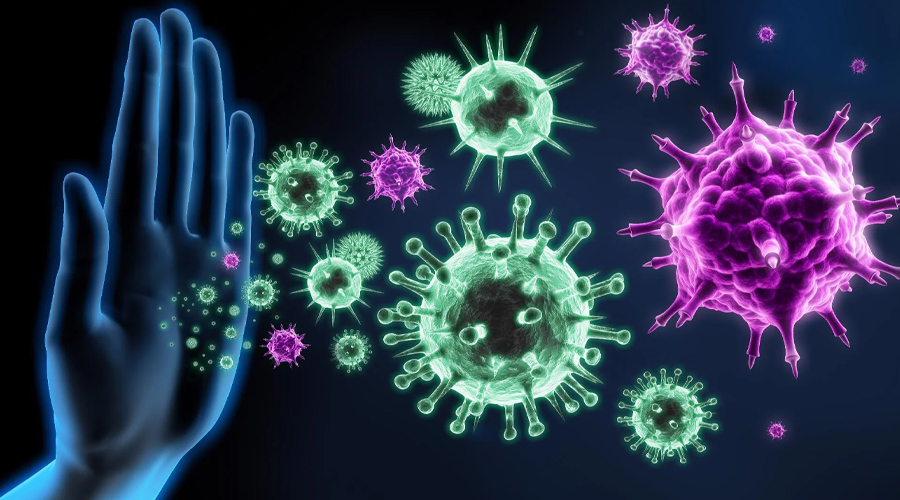
Certain factors like poor diet, stress, lack of sleep, and smoking can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to illnesses.
Signs like numbness, swelling, or fatigue may indicate a circulatory issue, affecting blood flow. Early detection can help prevent serious health problems.
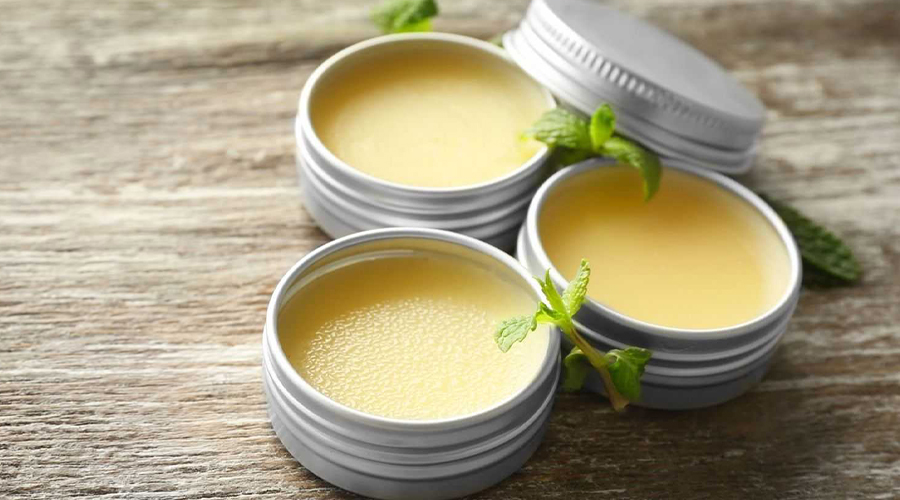

For best results, apply HillVital balms to clean skin, massage gently, and use regularly. Follow instructions for targeted relief and maximum effectiveness.